It can be used which of the following accounts is a liability? to finance payroll, payables, inventories, and other short-term liabilities. Ideally, suppliers would like shorter terms so they’re paid sooner rather than later because this helps their cash flow. Suppliers may offer companies discounts for paying on time (or early).

Non-current Liabilities
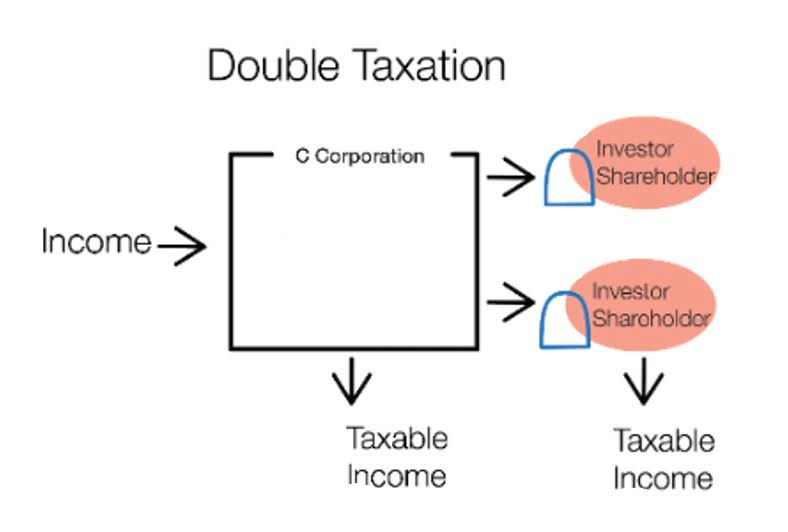
A liability is anything that’s borrowed from, owed to, or obligated to someone else. It can be real like a bill that must be paid or potential such as a possible lawsuit. A company might take out debt to expand and grow its business or an individual may take out a mortgage to purchase a home. The outstanding money that the restaurant owes to its wine supplier is considered a liability. The wine supplier considers the money it is owed to be an asset. We will discuss more liabilities in depth later in the accounting course.

AccountingTools
Debt financing is often used to fund operations or expansions. These debts usually arise from business transactions like purchases of goods and services. For example, a business looking to purchase a building will usually take out a mortgage from a bank in order to afford the purchase. The business then owes the bank for the mortgage and contracted interest. Suppose, for example, that two companies in the same industry have the same total debt. However, if one of those company’s debt is mostly short-term debt, it might run into cash flow issues if not enough revenue is generated to meet its obligations.
Types of Liability Accounts – Examples
In short, a company needs to generate enough revenue and cash in the short term to cover its current liabilities. The current ratio is a measure of liquidity that compares all of a company’s current assets to its current liabilities. If the ratio of current assets over current liabilities is greater than 1.0, it indicates that the company has enough available to cover its short-term debts and obligations. Typically, vendors https://maistor-kz.com/getting-started-financial-statements/ provide terms of 15, 30, or 45 days for a customer to pay. This means that the buyer can receive supplies but pay for them at a later date.
Examples of Current Liabilities
- The current portion of long-term debt due within the next year is also listed as a current liability.
- These invoices are recorded in accounts payable and act as a short-term loan from a vendor.
- These utility expenses are accrued and paid in the next period.
- Bonds are essentially contracts to pay the bondholders the face amount plus interest on the maturity date.
- Short-term debt is all debt payments owed within the next year.
- In accounting, financial liabilities are linked to past transactions or events that will provide future economic benefits.
The current portion of long-term debt due within the next year is also listed as a current liability. Notes Payable – A note payable is a long-term contract to borrow money from a creditor. The most common notes payable are mortgages and personal notes. Bonds Payable – Many companies choose to issue bonds to the public in order to finance future growth. Bonds are essentially contracts to pay the bondholders the face amount plus interest on the maturity date.
Accrued Expenses
AT&T clearly defines its bank debt that’s maturing in less than one year under current liabilities. Liabilities appear on the balance sheet, while expenses are on the income statement. Expenses relate to operational costs, unlike liabilities, which are debts owed. A 15-year mortgage is a long-term liability, but payments due this year are current liabilities.
- Conversely, companies might use accounts payable as a way to boost their cash.
- Unearned revenue arises when a company sells goods or services to a customer who pays the company but doesn’t receive the goods or services.
- Suppliers may offer companies discounts for paying on time (or early).
- AP typically carries the largest balances because they encompass day-to-day operations.
- If it is expected to be settled in the short-term (normally within 1 year), then it is a current liability.
- Current liabilities are usually considered short-term.
Liabilities
Right now it’s important just to know the basic concepts. Let’s look at a historical example using AT&T’s (T) 2020 balance sheet. The current/short-term liabilities are separated from long-term/non-current liabilities. The dividends declared by a company’s board of directors that have yet to be paid out to shareholders get recorded as current liabilities. Assets are what a company owns or something that’s owed to the company.

Lawsuits and the threat of lawsuits are the most common contingent liabilities but unused gift cards, product warranties, and recalls also fit into this category. Current liabilities are usually considered short-term. They’re expected to be concluded within 12 months or less.
How Are Current Liabilities Different From Long-Term Non-Current Ones?
- Typically, vendors provide terms of 15, 30, or 45 days for a customer to pay.
- Liabilities represent what you owe to others, whether as a financial obligation due to borrowing or as a legal commitment.
- A liability is anything that’s borrowed from, owed to, or obligated to someone else.
- They’re recorded in the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet.
- By allowing a company time to pay off an invoice, the company can generate revenue from the sale of the supplies and manage its cash needs more effectively.
- Here is a list of current and non-current liabilities.
- The current month’s utility bill is usually due the following month.
Accrued Expenses – Since accounting periods rarely fall directly after an expense period, companies often incur expenses but don’t pay them until the next period. The current month’s utility bill is usually due the following month. Once the utilities are used, the company owes the utility company. These utility expenses Outsource Invoicing are accrued and paid in the next period. Companies may also issue commercial paper (CP), a short-term, unsecured promissory note that’s used to raise funds. Commercial paper is a form of unsecured, short-term debt.